Bootstrap Modal Popup Jquery
Intro
Oftentimes, if we set up our web pages there is this type of material we do not like to happen on them until it is definitely really required by the guests and whenever that time comes they should have the capacity to just take a natural and basic activity and receive the required information in a matter of minutes-- fast, handy and on any sort of display screen size. Once this is the situation the HTML5 has just the best feature-- the modal. ( helpful hints)
Important details to consider:
Before beginning having Bootstrap's modal element, be sure to read the following since Bootstrap menu decisions have currently replaced.
- Modals are built with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. They are actually located above everything else in the documentation and remove scroll from the
<body>- Clicking on the modal "backdrop" will immediately finalize the modal.
- Bootstrap simply just supports one modal screen at a time. Nested modals usually are not provided as we think them to remain weak user experiences.
- Modals usage
position:fixeda.modal- One again , because of
position: fixed- In conclusion, the
autofocusKeep checking out for demos and usage suggestions.
- Due to how HTML5 identifies its own semantics, the autofocus HTML attribute has no effect in Bootstrap Modal Popup Position. To achieve the identical effect, use some custom JavaScript:
$('#myModal').on('shown.bs.modal', function ()
$('#myInput').focus()
)Effective ways to put into action the Bootstrap Modal Popup Form:
Modals are perfectly sustained in recent 4th version of one of the most well-known responsive framework-- Bootstrap and can easily as well be styled to reveal in a variety of dimensions according to developer's wishes and visual sense but we'll go to this in just a minute. Primary let's discover effective ways to create one-- step by step.
Initially we require a container to quickly wrap our disguised content-- to create one create a
<div>.modal.fadeYou really need to include certain attributes as well-- such as an original
id=" ~the modal unique name ~ "tabindex=" -1 "Tab.modal-dialog.modal-lg.modal-smNext we want a wrapper for the real modal content having the
.modal-content.modal-header<button>.closedata-dismiss="modal"<span>×<h1>-<h6>.modal-titleRight after changing the header it is certainly time for building a wrapper for the modal content -- it should take place along with the header component and have the
.modal-body.modal-footerdata-dismiss="modal"Now as soon as the modal has been built it is really time for establishing the element or elements which in turn we are willing to use to fire it up or in shorts-- create the modal show up in front of the viewers once they make the decision that they want the information held in it. This normally gets accomplished with a
<button>data-toggle = "modal"data-target = " ~ the unique ID attribute of the modal element we need to fire ~ "Approaches
.modal(options)
.modal(options)Triggers your material as a modal. Takes an optional options
object$('#myModal').modal(
keyboard: false
).modal('toggle')
.modal('toggle')Manually button a modal. Go back to the user just before the modal has in fact been presented or covered (i.e. right before the
shown.bs.modalhidden.bs.modal$('#myModal').modal('toggle').modal('show')
.modal('show')Manually begins a modal. Returns to the user just before the modal has literally been displayed (i.e. before the
shown.bs.modal$('#myModal').modal('show').modal('hide')
.modal('hide')Manually conceals a modal. Go back to the user before the modal has in fact been covered up (i.e. just before the
hidden.bs.modal$('#myModal').modal('hide')Bootstrap modals events
Bootstrap's modal class introduces a handful of events for entraping into modal performance. All modal events are fired at the modal in itself (i.e. at the
<div class="modal">$('#myModal').on('hidden.bs.modal', function (e)
// do something...
)Final thoughts
Essentially that is actually all of the critical points you should take care about if designing your pop-up modal component with the current 4th edition of the Bootstrap responsive framework-- right now go find an item to cover up in it.
Check out a few video information regarding Bootstrap Modal Popup:
Related topics:
Bootstrap Modal Popup: authoritative documents
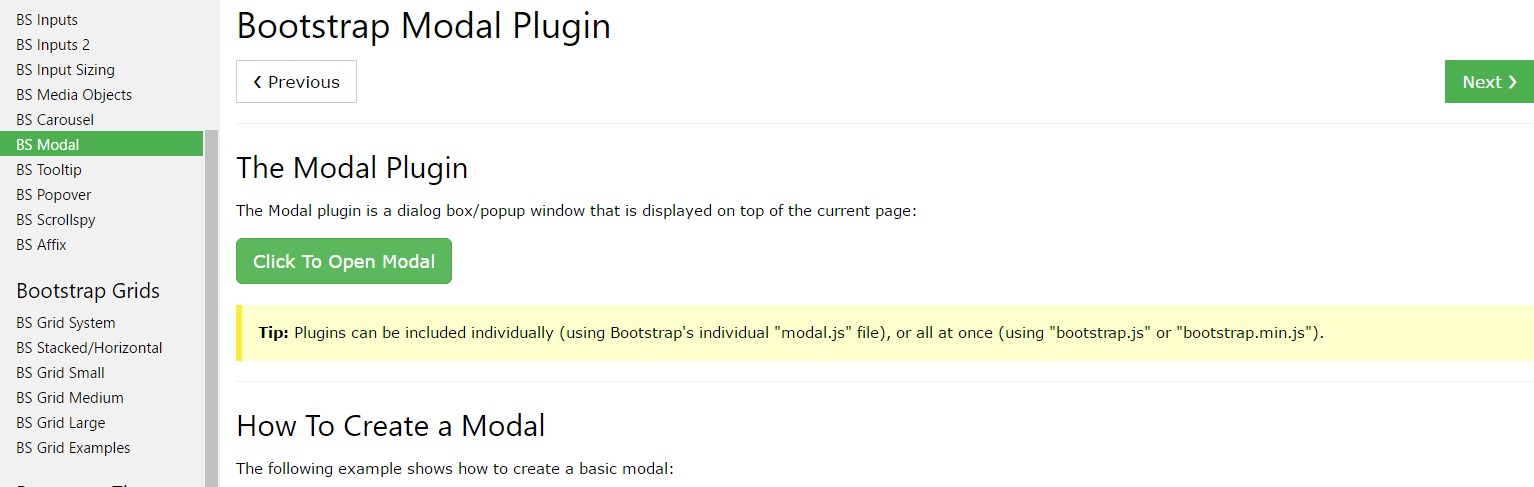
Bootstrap Modal Popup: training short training
Yet another handy content regarding to Bootstrap Modal Popup

